1189.”气球”的最大数量
给你一个字符串 text,你需要使用 text 中的字母来拼凑尽可能多的单词 “balloon”(气球)。
字符串 text 中的每个字母最多只能被使用一次。请你返回最多可以拼凑出多少个单词 **”balloon”**。
示例 1:

1
2
| 输入:text = "nlaebolko"
输出:1
|
示例 2:

1
2
| 输入:text = "loonbalxballpoon"
输出:2
|
示例 3:
1
2
| 输入:text = "leetcode"
输出:0
|
提示:
1 <= text.length <= 10^4text 全部由小写英文字母组成
解法1:
简单题。
思路:
创建一个hash表来存各个字母的出现次数,找a,b,l/2,o/2,n的最小值
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
| class Solution {
public:
int maxNumberOfBalloons(string text) {
int n=text.size();
vector<int> res(26,0);
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
{
res[text[i]-'a']++;
}
int mins=INT_MAX;
mins=min(mins,res[0]);
mins=min(mins,res[1]);
mins=min(mins,res[11]/2);
mins=min(mins,res[13]);
mins=min(mins,res[14]/2);
return mins;
}
};
|
1190.反转每对括号间的子串
给出一个字符串 s(仅含有小写英文字母和括号)。
请你按照从括号内到外的顺序,逐层反转每对匹配括号中的字符串,并返回最终的结果。
注意,您的结果中 不应 包含任何括号。
示例 1:
1
2
| 输入:s = "(abcd)"
输出:"dcba"
|
示例 2:
1
2
| 输入:s = "(u(love)i)"
输出:"iloveu"
|
示例 3:
1
2
| 输入:s = "(ed(et(oc))el)"
输出:"leetcode"
|
示例 4:
1
2
| 输入:s = "a(bcdefghijkl(mno)p)q"
输出:"apmnolkjihgfedcbq"
|
提示:
0 <= s.length <= 2000s 中只有小写英文字母和括号- 我们确保所有括号都是成对出现的
解法1:栈
思路:用栈存左括号出现位置,当遇见右括号时,翻转从栈顶值左括号到这个右括号的子串。
再遍历一遍字符串,将不是左右括号的字符挨个存入结果字符串。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
| class Solution {
public:
string reverseParentheses(string s) {
stack<int> st;
string res="";
int n=s.length();
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
{
if(s[i]=='(')
st.push(i);
else if(s[i]==')')
{
int t=st.top();
st.pop();
reverse(s.begin()+t,s.begin()+i);
}
}
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
{
if(s[i]!='('&&s[i]!=')')
res+=s[i];
}
return res;
}
};
|
1191.K次串联后最大子数组之和
给你一个整数数组 arr 和一个整数 k。
首先,我们要对该数组进行修改,即把原数组 arr 重复 k 次。
举个例子,如果 arr = [1, 2] 且 k = 3,那么修改后的数组就是 [1, 2, 1, 2, 1, 2]。
然后,请你返回修改后的数组中的最大的子数组之和。
注意,子数组长度可以是 0,在这种情况下它的总和也是 0。
由于 结果可能会很大,所以需要 模(mod) 10^9 + 7 后再返回。
示例 1:
1
2
| 输入:arr = [1,2], k = 3
输出:9
|
示例 2:
1
2
| 输入:arr = [1,-2,1], k = 5
输出:2
|
示例 3:
1
2
| 输入:arr = [-1,-2], k = 7
输出:0
|
提示:
1 <= arr.length <= 10^51 <= k <= 10^5-10^4 <= arr[i] <= 10^4
解法1:前缀和,后缀和
先计算出arr数组的总和,然后分两种情况进行讨论
1.若sum>0&&k>2
这种情况我们可以求出arr数组的最大前缀和(即复制到最右边的数组应该取的值)和最大后缀和(即最左边数组应该取的值)因为中间每个arr的和sum>0所以我们肯定要加上每个sum。
2.
(1).若k>1,我们复制一次arr。
(2)找到arr这个数组的最大子序和即为所求结果。
注意:中间数字用int会溢出,所以我们用long long 存数组,最后结果mod10^9+7.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
| class Solution {
public:
int kConcatenationMaxSum(vector<int>& arr, int k) {
int mod=pow(10,9)+7;
int n=arr.size();
vector<long long> sum(n+1,0);
for(int i=1;i<n+1;i++)
{
sum[i]=sum[i-1]+arr[i-1];
}
long long res=0;
if(sum[n]>0&&k>2)
{
long long frist=0,last=0;
for(int i=0;i<n+1;i++)
{
frist=max(frist,sum[n]-sum[n-i]);
last=max(last,sum[i]);
}
res=frist+last+(k-2)*sum[n];
}
else
{
vector<int> temp(arr);
if(k>1)
{
for(auto x:arr)
{
temp.push_back(x);
}
}
long long sum_t=0;
for(int i=0;i<temp.size();i++)
{
if(sum_t>0)
sum_t+=temp[i];
else sum_t=temp[i];
res=max(res,sum_t);
}
}
return res%mod;
}
};
|
1192.查找集群内的「关键连接」
力扣数据中心有 n 台服务器,分别按从 0 到 n-1 的方式进行了编号。
它们之间以「服务器到服务器」点对点的形式相互连接组成了一个内部集群,其中连接 connections 是无向的。
从形式上讲,connections[i] = [a, b] 表示服务器 a 和 b 之间形成连接。任何服务器都可以直接或者间接地通过网络到达任何其他服务器。
「关键连接」是在该集群中的重要连接,也就是说,假如我们将它移除,便会导致某些服务器无法访问其他服务器。
请你以任意顺序返回该集群内的所有 「关键连接」。
示例 1:
1
2
3
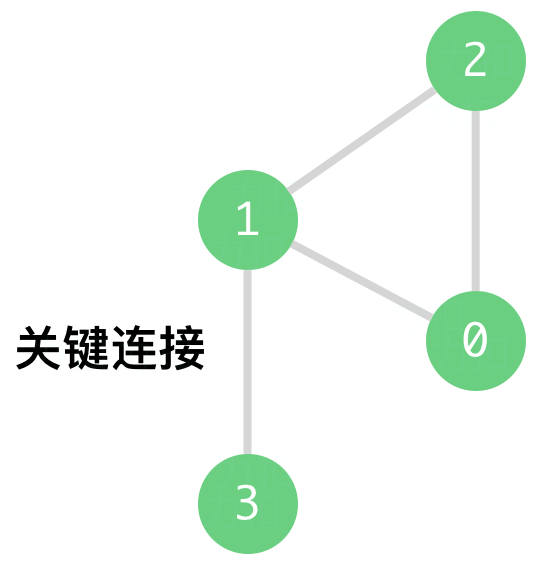
| 输入:n = 4, connections = [[0,1],[1,2],[2,0],[1,3]]
输出:[[1,3]]
解释:[[3,1]] 也是正确的。
|
提示:
1 <= n <= 10^5n-1 <= connections.length <= 10^5connections[i][0] != connections[i][1]- 不存在重复的连接
解法1:Tarjan算法
找到图中的割点问题。用Tarjan算法实现。
算法实现步骤:
1.定义dfn[i]数组表示dfs遍历时的i点的次序从1开始
2.定义low[i]数组表示i点不经过父节点能到达编号最小的点的数值
3.定义father[i]数组表示i点的父节点
4.遍历connections数组将每个边的两端记录下来。然后进行tarjan算法。
tarjan算法:
对每个点设置父节点,dfs遍历次序dfn[i]的值,默认low[i]值为dfs[i],对与i直接相连的点进行遍历,设为to,
(1)to为父节点跳过,
(2)dfn[to]==-1表示还未遍历,进行tarjan(to,i),然后low[i]在low[i]和low[to]选择一个最小值
(3)若已经遍历dfn[to] low[i]在low[i]和dfn[to]选择一个最小值
5.进行完tarjan算法,遍历所有点,判断父节点dfn[f]和low[i]关系,若low[i]>dfn[f]表示i点必须经过父节点f才能访问到f也就意味着(i,f)这条边是一个割边。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
| class Solution {
private:
vector<vector<int>> _g;
vector<int> _low;
vector<int> _dfn;
vector<int> _father;
int time;
public:
vector<vector<int>> criticalConnections(int n, vector<vector<int>>& connections) {
vector<vector<int>> g(n+1);
vector<int> low(n+1,-1);
vector<int> dfn(n+1,-1);
vector<int> father(n+1);
vector<vector<int>> res;
if(n==1)
return res;
this->_g=g;
this->_low=low;
this->_dfn=dfn;
this->_father=father;
time=0;
for(auto temp:connections)
{
int from=temp[0]+1,to=temp[1]+1;
_g[from].push_back(to);
_g[to].push_back(from);
}
tarjan(1,0);
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
int f=_father[i];
if(f>0&&_low[i]>_dfn[f])
{
vector<int> re;
re.push_back(i-1);
re.push_back(f-1);
res.push_back(re);
}
}
return res;
}
void tarjan(int i,int ifather)
{
_father[i]=ifather;
time++;
_low[i]=time;
_dfn[i]=time;
for(int j=0;j<_g[i].size();j++)
{
int to=_g[i][j];
if(ifather==to)
continue;
if(_dfn[to]==-1)
{
tarjan(to,i);
_low[i]=min(_low[i],_low[to]);
}
else
_low[i]=min(_low[i],_dfn[to]);
}
}
};
|


